War is a costly endeavor, not just in terms of human lives but also financially. To fund their military campaigns, countries often resort to various means, one of which is issuing war bonds. In this article, we will explore the concept of war bonds, their historical significance, their impact on the economy, and their role in supporting the United States’ war efforts.
Introduction
War bonds, also known as defense bonds or liberty bonds, are financial instruments issued by governments during times of war to raise funds from their citizens. These bonds allow individuals to lend money to their government, essentially investing in the war effort. In return, bondholders receive interest on their investment and the promise of repayment at a future date.
What are War Bonds?
War bonds are essentially loans made by individuals to their government. When a government issues war bonds, it is essentially borrowing money from its citizens to finance the war. The bondholders become creditors of the government and are entitled to receive interest payments over time. Once the war is over, the government repays the principal amount to the bondholders.
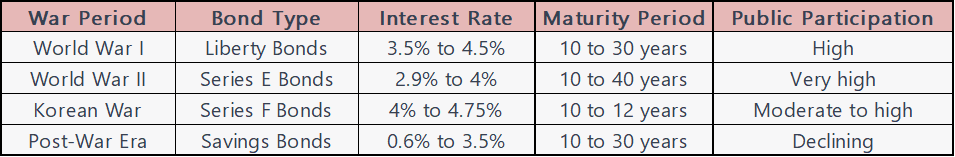
Note: The interest rates and maturity periods mentioned in the table are approximate and can vary based on specific bond series and market conditions.
History of War Bonds
World War I
The concept of war bonds gained prominence during World War I. Governments, including the United States, turned to their citizens for financial support to cover the enormous costs of the war. In the U.S., the government launched several bond drives, appealing to patriotism and a sense of duty to contribute to the war effort. These bonds played a crucial role in financing the war and rallying public support.
World War II
War bonds reached their peak during World War II. The U.S. government introduced the Series E bond program, which allowed citizens to contribute as little as $25 to support the war. The bond drives were accompanied by extensive propaganda campaigns, celebrity endorsements, and patriotic rallies, all aimed at encouraging citizens to invest in war bonds. These efforts proved highly successful and played a significant role in financing the war.
Post-War Period
Following World War II, war bonds continued to be issued by the U.S. government to help finance the reconstruction efforts and manage the national debt. However, the popularity of war bonds gradually declined as the economy stabilized and alternative investment opportunities became more attractive.
Purpose and Benefits of War Bonds
The primary purpose of war bonds is to raise funds for the war effort. By encouraging citizens to invest in bonds, governments can tap into the collective financial resources of the nation. War bonds offer several benefits, both to the government and the bondholders:
- Financial Support: War bonds provide governments with a crucial source of funding to cover the costs of war, including the purchase of weapons, equipment, and the provision of essential services.
- Patriotic Contribution: Investing in war bonds allows citizens to contribute directly to their country’s war efforts, fostering a sense of patriotism and unity.
- Interest Income: Bondholders receive regular interest payments on their investment, providing them with a source of income during the war period.
- Safe Investment: War bonds are generally considered safe investments as they are backed by the full faith and credit of the government. This reassures investors about the security of their funds.
Types of War Bonds
Over the years, different types of war bonds have been issued by the U.S. government. Let’s explore some of the notable ones:
Series E Bonds
Series E bonds were introduced during World War II and became the most popular type of war bond. These bonds were sold at a discount to their face value and reached maturity after a fixed period, typically ten years. Series E bonds provided a reliable investment opportunity for the general public.
Series F Bonds
Series F bonds were a follow-up to Series E bonds, introduced in 1952 during the Korean War. These bonds featured a higher interest rate and maturity period than Series E bonds, making them an attractive investment option for those looking for greater returns.
Victory Bonds
Victory bonds were issued during both World War I and World War II. These bonds were sold to finance specific war-related expenses and were often accompanied by aggressive marketing campaigns aimed at instilling a sense of patriotism and urgency in potential bond buyers.
How War Bonds Helped Fund the War Effort
War bonds played a critical role in financing the war efforts of the United States. The funds raised through war bond drives were used to:
- Purchase military equipment, ammunition, and supplies.
- Provide financial support to soldiers and their families.
- Fund research and development of new technologies.
- Support infrastructure projects related to the war effort.
- Manage the national debt and maintain economic stability.
The collective contributions of individuals investing in war bonds made a significant impact on the country’s ability to sustain its military operations.
Promoting War Bonds
To encourage citizens to invest in war bonds, governments employed various strategies and campaigns to create awareness and promote their sale. Some of the notable methods used during World War II included:
- Propaganda Campaigns: Governments used powerful propaganda campaigns to instill a sense of duty, patriotism, and urgency among citizens. Posters, films, and other media were employed to convey the message that buying war bonds was a vital part of the war effort.
- Celebrity Endorsements: Celebrities, including movie stars, musicians, and athletes, were often enlisted to endorse war bonds and appear in promotional materials. Their influence and popularity helped generate enthusiasm and encouraged public participation.
- War Bond Rallies: Large-scale rallies and events were organized to engage the public and create a festive atmosphere around purchasing war bonds. These events often featured speeches, performances, and parades, all aimed at promoting the bonds and boosting sales.
The Impact of War Bonds on the Economy
War bonds had a significant impact on the economy, both during and after the war period. Here are some ways in which war bonds influenced the economy:
- Stimulating Savings: War bonds encouraged individuals to save their money rather than spend it. This increased the pool of available capital and promoted a savings culture among the general population.
- Controlling Inflation: By channeling funds into war bonds, governments could effectively reduce the money supply circulating in the economy. This helped control inflation and stabilize prices during times of war.
- Debt Management: War bonds provided a mechanism for managing the national debt incurred during war periods. Bond sales helped offset the financial burden on the government, reducing the need for excessive borrowing.
Successes and Challenges of War Bond Drives
War bond drives were met with varying degrees of success and faced their fair share of challenges. While the campaigns during World War II were highly successful in generating public support, subsequent war bond drives encountered difficulties due to changing economic conditions and evolving investment preferences.
Some of the factors that contributed to the success of war bond drives include:
- Patriotic Sentiment: During times of war, patriotism runs high, and citizens are more willing to contribute to the war effort. The emotional appeal of supporting the troops and defending the nation fueled public participation.
- Effective Marketing and Propaganda: The skillful use of marketing techniques and propaganda campaigns helped create a sense of urgency and importance around investing in war bonds. These efforts effectively tapped into the emotions and values of the public.
- Celebrity Influence: The involvement of popular celebrities and influential figures boosted the credibility and appeal of war bonds. Their endorsements and participation in events garnered public attention and encouraged bond sales.
However, war bond drives also faced challenges, including:
- Competition from Other Investments: As the economy stabilized post-war, alternative investment opportunities emerged, attracting the attention of investors. This shift in investment preferences made it more challenging to sustain the momentum of war bond drives.
- Changing Economic Conditions: Economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and market fluctuations influenced the attractiveness of war bonds as investment options. Fluctuations in these factors could affect public interest in purchasing war bonds.
Legacy of War Bonds
The legacy of war bonds extends beyond their immediate impact during times of war. Some notable aspects of their legacy include:
- National Unity and Patriotism: War bonds symbolize the collective sacrifice and commitment of citizens to their nation. They serve as a reminder of the unity and resilience demonstrated during challenging times.
- Financial Education and Savings Culture: War bond campaigns encouraged financial literacy and savings habits among the public. They emphasized the importance of saving for the future and instilled a sense of responsibility in managing personal finances.
- Historical Significance: War bonds are a testament to the nation’s history and the efforts made by previous generations to support their country. They serve as a tangible link to significant events and reflect the values and ideals of the time.
Investing in War Bonds Today
While war bonds are no longer actively issued in the United States, there are other ways individuals can invest in the country’s growth and security. Government bonds, treasury bonds, and other fixed-income securities are available for investment, offering a secure means of supporting the nation’s financial stability and economic development.
Investors can explore these options through financial institutions or consult with financial advisors to make informed decisions based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
War bonds have played a crucial role in supporting the United States’ war efforts throughout history. These financial instruments have allowed citizens to contribute directly to their country’s defense, fostered a sense of patriotism, and helped finance military campaigns. The impact of war bonds extends beyond their financial significance, encompassing national unity, economic stability, and a legacy of resilience. While war bonds are no longer issued, the spirit of supporting the nation’s growth and security remains relevant through various investment opportunities available today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Are war bonds still available for purchase? A1: No, war bonds are no longer actively issued. However, there are other investment options available, such as government bonds and treasury securities.
Q2: Did war bonds have a significant impact on financing the war efforts? A2: Yes, war bonds played a significant role in financing wars, including World War I and World War II. They provided crucial funds for the purchase of military equipment, infrastructure development, and support for soldiers and their families.
Q3: Did war bonds offer any benefits to the bondholders? A3: Yes, war bondholders received regular interest payments on their investments and the promise of repayment at a future date. War bonds provided a safe investment option backed by the government.
Q4: How were war bonds promoted during World War II? A4: War bonds were promoted through extensive propaganda campaigns, celebrity endorsements, and large-scale rallies. These efforts aimed to create awareness, generate public support, and foster a sense of patriotism.
Q5: What is the legacy of war bonds? A5: War bonds represent national unity, patriotism, and a savings culture. They hold historical significance and serve as a reminder of the collective sacrifices made by citizens in times of war.



