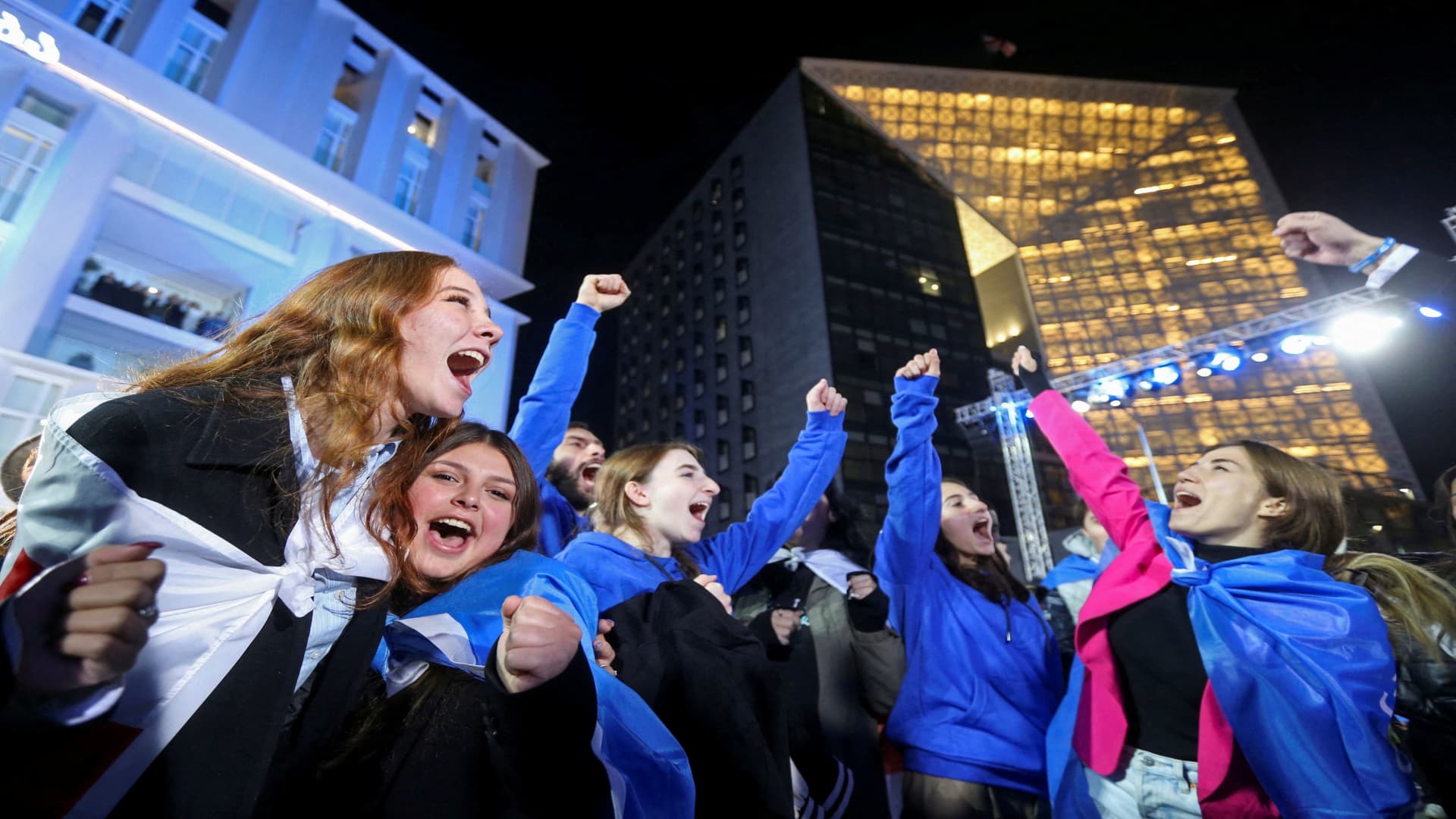Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, managing personal finances has become more crucial than ever. Salaried employees often encounter various financial challenges and make mistakes that can have long-term consequences on their financial well-being. This article aims to highlight 20 common financial mistakes made by salaried employees and provide actionable tips to avoid them. By understanding and avoiding these pitfalls, individuals can take control of their finances and pave the way for a more secure future.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of Financial Management
- Mistake 1: Living Beyond Means
- Mistake 2: Neglecting Budgeting
- Mistake 3: Failing to Save for Emergencies
- Mistake 4: Accumulating High-Interest Debt
- Mistake 5: Overusing Credit Cards
- Mistake 6: Ignoring Retirement Planning
- Mistake 7: Neglecting Insurance Coverage
- Mistake 8: Not Investing Wisely
- Mistake 9: Disregarding Tax Planning
- Mistake 10: Being Underinsured or Overinsured
- Mistake 11: Impulsive and Emotional Spending
- Mistake 12: Overlooking Financial Literacy
- Mistake 13: Ignoring Investment Diversification
- Mistake 14: Taking on Unmanageable Housing Costs
- Mistake 15: Not Negotiating Salary and Benefits
- Mistake 16: Failing to Set Financial Goals
- Mistake 17: Procrastinating Estate Planning
- Mistake 18: Overlooking Employee Benefits
- Mistake 19: Neglecting Regular Financial Checkups
- Mistake 20: Lack of Continual Learning and Adaptation
Understanding the Importance of Financial Management
Proper financial management is vital for everyone, especially salaried employees. By avoiding common financial mistakes, individuals can create a strong foundation for their financial future. Let’s delve into each of the 20 financial mistakes in detail and understand how to prevent them.
Mistake 1: Living Beyond Means
One of the most significant financial mistakes individuals make is living beyond their means. This occurs when expenses exceed income, leading to a never-ending cycle of debt. It is crucial to establish a realistic budget that accounts for all expenses and ensures income covers them.
Mistake 2: Neglecting Budgeting
Without a well-planned budget, it is easy to lose track of spending and fall into financial trouble. Budgeting helps allocate income efficiently, plan for essential expenses, and save for the future. Tracking expenses and setting financial goals can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions.
Mistake 3: Failing to Save for Emergencies
Unexpected emergencies, such as medical bills or job loss, can disrupt financial stability. Failing to build an emergency fund can result in relying on credit cards or loans, accumulating debt. Setting aside a portion of income regularly for emergencies provides a safety net during challenging times.
Mistake 4: Accumulating High-Interest Debt
Using credit irresponsibly and accumulating high-interest debt can be detrimental to financial health. High interest rates can quickly spiral out of control, leading to a significant financial burden. Minimizing the use of credit cards and paying off debt promptly should be a priority.
Mistake 5: Overusing Credit Cards
Credit cards can be a convenient payment method, but misusing them can lead to financial distress. Relying too heavily on credit cards without a repayment plan can result in mounting debt. It is advisable to use credit cards responsibly and pay off the balance in full each month.
Mistake 6: Ignoring Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is often neglected by salaried employees, leading to financial insecurity in later years. Contributing to retirement accounts, such as 401(k) or individual retirement accounts (IRAs), is crucial for building a substantial retirement corpus. Starting early and taking advantage of employer matching programs can greatly benefit long-term financial well-being.
Mistake 7: Neglecting Insurance Coverage
Insurance provides protection against unforeseen events and helps mitigate financial risks. Neglecting insurance coverage, whether for health, life, or property, can leave individuals vulnerable to substantial financial losses. Evaluating insurance needs and securing adequate coverage is essential.
Mistake 8: Not Investing Wisely
Failing to invest wisely can hinder wealth accumulation and financial growth. Investing allows money to work for individuals, generating returns over time. Understanding investment options, diversifying portfolios, and seeking professional advice can help optimize investment decisions.
Mistake 9: Disregarding Tax Planning
Tax planning is often overlooked but can significantly impact one’s financial situation. Failing to take advantage of available deductions and credits can result in higher tax liabilities. Engaging with tax professionals or using tax software can help optimize tax planning and maximize savings.
Mistake 10: Being Underinsured or Overinsured
Maintaining an appropriate level of insurance coverage is crucial. Being underinsured can leave individuals exposed to financial risks, while being overinsured can result in unnecessary expenses. Regularly reviewing insurance policies and adjusting coverage based on changing circumstances is advisable.
Mistake 11: Impulsive and Emotional Spending
Impulsive and emotional spending can quickly derail financial plans. Giving in to immediate desires without considering long-term consequences can lead to financial instability. Practicing mindful spending and distinguishing between needs and wants can help avoid unnecessary expenses.
Mistake 12: Overlooking Financial Literacy
Lack of financial literacy can be a significant hurdle in achieving financial goals. Understanding personal finance concepts, such as budgeting, investing, and debt management, is essential. Continual learning through books, articles, or financial courses can improve financial decision-making.
Mistake 13: Ignoring Investment Diversification
Investing in a single asset class or failing to diversify investments can expose individuals to unnecessary risks. Diversification spreads investments across different assets, reducing the impact of market volatility. Creating a diversified investment portfolio can provide stability and potentially higher returns.
Mistake 14: Taking on Unmanageable Housing Costs
Housing costs, such as mortgage payments or rent, often form a significant portion of an individual’s expenses. Committing to unmanageable housing costs can strain finances and limit other opportunities. Carefully assessing housing affordability based on income and long-term financial goals is crucial.
Mistake 15: Not Negotiating Salary and Benefits
Neglecting to negotiate salary and benefits can result in missed opportunities for financial growth. Salaried employees should advocate for themselves during the hiring process or when considering promotions. Researching market salaries and showcasing skills and achievements can lead to improved compensation packages.
Mistake 16: Failing to Set Financial Goals
Without clear financial goals, it becomes challenging to make sound financial decisions. Setting short-term and long-term goals provides direction and motivation. Well-defined goals, such as saving for a down payment or funding education, help prioritize financial actions.
Mistake 17: Procrastinating Estate Planning
Estate planning involves preparing for the distribution of assets after one’s passing. Procrastinating estate planning can lead to complications and financial burdens for loved ones. Creating wills, establishing trusts, and naming beneficiaries are essential steps for preserving wealth and ensuring a smooth transfer of assets.
Mistake 18: Overlooking Employee Benefits
Salaried employees often receive various benefits from their employers, such as healthcare plans, retirement contributions, or stock options. Overlooking or underutilizing these benefits can result in missed opportunities to enhance financial well-being. Understanding and taking full advantage of employee benefits is crucial.
Mistake 19: Neglecting Regular Financial Checkups
Financial situations change over time, and neglecting regular financial checkups can lead to missed opportunities or financial inefficiencies. Reviewing and reassessing financial plans periodically helps identify areas for improvement, track progress, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Mistake 20: Lack of Continual Learning and Adaptation
The financial landscape is constantly evolving, and failing to stay informed can hinder financial growth. Engaging in continual learning, staying updated with industry trends, and adapting financial strategies accordingly can lead to better decision-making and improved financial outcomes.
Conclusion
Avoiding financial mistakes is essential for salaried employees to secure their financial future. By being mindful of budgeting, saving for emergencies, investing wisely, and staying financially educated, individuals can navigate their financial journey with confidence. Taking proactive steps to avoid these 20 common financial mistakes will lead to better financial stability and a brighter future.
Fequemtly Asked Questions
- What should salaried employees do to avoid living beyond their means?
To avoid living beyond their means, salaried employees should follow these steps:
- Create a realistic budget: Track income and expenses, and allocate funds for necessary expenses, savings, and debt repayment.
- Prioritize needs over wants: Distinguish between essential expenses and discretionary spending, and avoid unnecessary purchases.
- Save for emergencies: Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and avoid relying on credit cards or loans.
- Limit credit card usage: Use credit cards responsibly, pay off balances in full each month, and avoid accumulating high-interest debt.
- Practice mindful spending: Consider the long-term impact of purchases and make informed decisions based on financial goals.
- How can I start investing wisely as a salaried employee?
Here are some steps to start investing wisely as a salaried employee:
- Set financial goals: Define your investment objectives, such as saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding education.
- Educate yourself: Learn about different investment options, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with a financial advisor who can guide you based on your risk tolerance, goals, and timeline.
- Start with a diversified portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes to minimize risk.
- Invest regularly: Consistency is key; contribute a fixed amount regularly to take advantage of dollar-cost averaging.
- Monitor and review: Stay updated on your investments, assess performance, and make adjustments as needed.
- Why is it crucial for salaried employees to prioritize retirement planning?
Prioritizing retirement planning is crucial for salaried employees due to the following reasons:
- Long-term financial security: Retirement planning ensures that you have sufficient funds to maintain your desired lifestyle after you stop working.
- Compounding growth: Starting early allows your investments to grow exponentially through compounding over a long period.
- Social security may not be enough: Relying solely on social security may not provide enough income during retirement; personal savings and investments are necessary.
- Rising healthcare costs: Healthcare expenses tend to increase with age, and having a retirement plan can help cover these costs.
- Flexibility and peace of mind: By planning for retirement, you have the freedom to make choices based on your financial readiness and enjoy peace of mind in your golden years.
- What are the key benefits of diversifying investments?
Diversifying investments offers several benefits to salaried employees:
- Risk reduction: Spreading investments across different asset classes helps minimize the impact of a single investment’s poor performance.
- Enhanced returns: Diversification allows you to capture gains from various sectors or asset classes, potentially increasing overall returns.
- Protection against market volatility: Different assets often have varying responses to market conditions, providing a cushion during economic fluctuations.
- Income stability: A diversified portfolio can generate income from multiple sources, reducing dependency on a single investment or income stream.
- Opportunity for growth: Investing in different sectors or geographic regions increases the likelihood of benefiting from emerging markets or industry growth.
- How often should I review my financial plan and make adjustments?
It is recommended to review your financial plan regularly and make adjustments as needed. Here are some key points to consider:
- Major life events: Significant life changes, such as marriage, having children, or career shifts, may require adjustments to your financial plan.
- Annual review: Conduct a comprehensive review of your financial plan at least once a year to reassess goals, track progress, and make necessary changes.
- Investment performance: Monitor the performance of your investments regularly and rebalance your portfolio if it deviates from your desired asset allocation.
- Budget adjustments: Evaluate your budget periodically to ensure it aligns with your current financial situation and goals.
-
39-year-old makes about $18,000 a month in passive income without a college degree: ‘I work only 4 hours a day’
After dropping out of college in 2007, Amy Landino started a side hustle creating videos and doing social media. Ultimately she was able to quit her day job.
-
33-year-old mortician doesn’t fear death and is ‘wildly happy’ earning $87,000 a year: I haven’t ‘gone home sad a single day’
The first time Victor M. Sweeney observed an embalming, it was for an 18-year-old woman who had died in a car crash just before her high school graduation. At the …
-
All sides claim victory in Georgia election as exit polls give different results
Supporters of the Georgian Dream party celebrate at the party’s headquarters after the announcement of exit poll results in parliamentary elections, in Tbilisi, Georgia October 26, 2024.. Irakli Gedenidze | …
-
Biden says Elon Musk was an ‘illegal worker’ when he began U.S. career
Joe Biden, left, and Elon Musk. Evelyn Hockstein | Reuters; Andrew Harrer | Bloomberg | Getty Images. President Joe Biden called out Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, now a …
-
The Washington Post is in deep turmoil as Bezos remains silent on non-endorsement
New York CNN —. One day after The Washington Post announced it would not endorse a presidential candidate in this year’s election or in the future, its billionaire owner remains …
-
Welcome to the ‘show me the money’ quarter
New York CNN —. Silicon Valley’s biggest names are about to reveal if their massive artificial intelligence investments are paying off or just burning cash. And the timing couldn’t be …